Problem¶
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Follow up: Could you solve it without reversing the input lists?
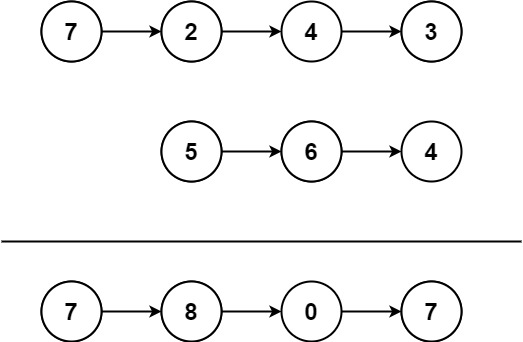
Example 1:
Solve¶
Remove link-list¶
Quick and fast solution is removing list link, as python handle the big integer by default (standard library) and way faster than loop through the linked list
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
n = 0
p = l1
while p:
n *= 10
n += p.val
p = p.next
m = 0
q = l2
while q:
m *= 10
m += q.val
q = q.next
result = n + m
if result == 0:
return ListNode(0)
head = None
while result > 0:
head = ListNode(result%10, head)
result //= 10
return head
¶
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
n = 0
p = l1
while p:
n *= 10
n += p.val
p = p.next
m = 0
q = l2
while q:
m *= 10
m += q.val
q = q.next
result = n + m
if result == 0:
return ListNode(0)
head = None
while result > 0:
head = ListNode(result%10, head)
result //= 10
return head
Forcing to use the linked list?¶
While there is no reason to do so (in Python). We can still do it for some challenge, using linked list as a big number handling.
Still, the provided input isn’t the best way to implement big number, here should be an ideal one:
class BigNumber:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.end = None
def toListNode(self):
result = ListNode()
p = self
while p:
result = ListNode(p.val, result)
p = p.next
return self.end
def add_number(self, val):
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.end = ListNode(val)
return
self.end.next = ListNode(val)
self.end = self.end.next
def add(self, otherBigNumber):
result = BigNumber()
p, q = self.end, otherBigNumber.end
carry = 0
while p or q:
val_1, val_2 = 0, 0
if p:
val_1 = p.val
p = p.next
if q:
val_2 = q.val
q = q.next
result.add_number((val_1 + val_2 + carry) % 10)
carry = (val_1 + val_2 + carry) // 10
if carry:
result.add_number(carry)
Class BigNumber is the implementation for O(1) insert, O(n) adding time complexity, where:
- The number representation in revert order: Number
123459will be storing as9 -> 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1. Which helpingaddfunction which also done in revert order. - To change the input to our crafted class, I create a
Helperfunction to revert the order of Linked ListListNodeand return correspondBigNumber
Here is final implementation
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class BigNumber:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.end = None
def add_number(self, val):
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.end = ListNode(val)
return
self.end.next = ListNode(val)
self.end = self.end.next
def toListNode(self):
result = None
p = self.head
while p:
result = ListNode(p.val, result)
p = p.next
return result
def add(self, otherBigNumber):
result = BigNumber()
p, q = self.head, otherBigNumber.head
carry = 0
while p or q:
val_1, val_2 = 0, 0
if p:
val_1 = p.val
p = p.next
if q:
val_2 = q.val
q = q.next
result.add_number((val_1 + val_2 + carry) % 10)
carry = (val_1 + val_2 + carry) // 10
if carry:
result.add_number(carry)
return result
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
def helper(p):
result = None
if p is None:
result = BigNumber()
else:
result = helper(p.next)
result.add_number(p.val)
return result
return helper(l1).add(helper(l2)).toListNode()
Comparing¶
Just don’t. It a basic to handle number operation in most of non support language. Most of the time you will want to use close to minimalism library or OS/Hardware standard (example https://gmplib.org/).
Created : August 16, 2023